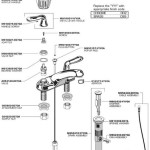
What Are The Parts of a Bathtub Faucet Called? A Detailed Diagram and Explanation
A bathtub faucet, seemingly a simple device, is actually composed of several interconnected parts, each playing a crucial role in delivering water at the desired temperature and flow rate. Understanding these components is beneficial for homeowners undertaking repairs, replacements, or even simply troubleshooting common issues. This article provides a detailed breakdown of the anatomy of a typical bathtub faucet, accompanied by explanations of each part's function.
While specific designs may vary, most bathtub faucets share a core set of components. This discussion will focus on the prevalent types, including compression faucets, ball faucets, cartridge faucets, and ceramic disc faucets, highlighting the fundamental parts common to them all. A diagram illustrating these parts further enhances understanding.
Before delving into the specific parts, it is important to differentiate between the various types of bathtub faucets. Compression faucets, the oldest and perhaps simplest design, rely on rubber washers to seal the water flow. Ball faucets utilize a slotted ball to control water mixing. Cartridge faucets employ a cartridge containing O-rings and seals to regulate water flow and temperature. Finally, ceramic disc faucets, the most modern, use two ceramic discs that slide over each other to control water flow.
Key Point 1: Identifying the Primary Components
The primary components of a bathtub faucet can be broadly categorized into the handle(s), spout, valve body, and associated hardware. Each of these categories encompasses several individual parts that work in concert.
Handles: The handle(s) control the flow and temperature of the water. A single-handle faucet controls both hot and cold water with one lever, while dual-handle faucets have separate handles for hot and cold water. The handle itself connects to the valve stem (in compression faucets) or the cartridge/ball mechanism in other types. Beneath the handle, you'll often find a decorative flange or escutcheon that covers the faucet body and provides a finished look. The handle is typically secured to the valve stem or cartridge with a screw, often concealed beneath a decorative cap.
Spout: The spout is the outlet through which water flows into the bathtub. Spouts come in various shapes and sizes, from simple curved designs to more elaborate gooseneck styles. The spout is connected to the valve body and directs the mixed water flow into the tub. A diverter, often located on the spout, allows the user to switch the water flow from the tub spout to the showerhead.
Valve Body: The valve body is the central housing that contains the working parts of the faucet. It is typically made of brass or another durable metal and is connected to the water supply pipes. The valve body houses the valve seats (in compression faucets), the ball assembly (in ball faucets), the cartridge (in cartridge faucets), or the ceramic discs (in ceramic disc faucets). The valve body also provides the connection points for the hot and cold water supply lines.
Associated Hardware: This category includes a variety of components such as screws, O-rings, washers, nuts, and mounting hardware. These parts are essential for securing the faucet to the bathtub and ensuring a watertight seal. O-rings and washers prevent leaks around the various connections, while mounting nuts and screws secure the faucet to the tub or surrounding surface.
A detailed diagram would show these interconnected parts. For example, the diagram would illustrate how the handle connects to the valve stem, which in turn interacts with the valve seat in a compression faucet. Similarly, the diagram would show how the cartridge is seated within the valve body in a cartridge faucet, and how the spout is secured to the valve body with a threaded connection and O-ring.
Key Point 2: Dissecting the Components of Different Faucet Types
While the primary components remain consistent, the specific parts within each type of faucet differ significantly, reflecting their distinct operational mechanisms.
Compression Faucet Parts: * Handle: Controls the valve stem rotation. * Handle Screw: Secures the handle to the valve stem. * Bonnet Nut: Holds the valve stem assembly in place within the faucet body. * Valve Stem: A threaded rod that moves up and down when the handle is turned. * Washer: A rubber or fiber ring that seals against the valve seat to stop water flow. * Valve Seat: A stationary surface against which the washer presses to stop water flow. Typically threaded into the valve body. * Spout: The outlet for the water. Typically threaded into the valve body. * O-rings: Provide a watertight seal around the valve stem and spout.
Ball Faucet Parts: * Handle: Controls the movement of the ball. * Adjusting Ring: Controls the tension on the ball, affecting the ease of handle movement. * Cam Assembly: Contains the cam and packing, which control water flow. * Ball: A slotted metal ball that rotates to control the mixing of hot and cold water. * Seats and Springs: Located beneath the ball, these provide a seal against the ball to prevent leaks. * Spout: The outlet for the water. Often includes a diverter. * O-rings: Provide a watertight seal around various components.
Cartridge Faucet Parts: * Handle: Controls the movement of the cartridge. * Handle Screw: Secures the handle to the cartridge stem. * Cartridge Retaining Clip: Secures the cartridge within the valve body. * Cartridge: A self-contained unit containing O-rings and seals that control water flow and temperature. * Spout: The outlet for the water. Often includes a diverter. * O-rings: Provide a watertight seal around the cartridge and spout.
Ceramic Disc Faucet Parts: * Handle: Controls the movement of the ceramic discs. * Handle Screw: Secures the handle to the cartridge stem. * Cylinder Cartridge: Contains the ceramic discs. * Ceramic Discs: Two highly polished ceramic discs that slide over each other to control water flow. * Seals: Provide a watertight seal around the ceramic discs. * Spout: The outlet for the water. Often includes a diverter. * O-rings: Provide a watertight seal around the cartridge and spout.
A detailed diagram for each faucet type would clearly illustrate the placement and function of these individual parts. The diagram would show, for example, the precise location of the seats and springs in a ball faucet, or the arrangement of the ceramic discs within the cylinder cartridge of a ceramic disc faucet. Furthermore, the diagram would highlight the importance of the O-rings in maintaining watertight seals in each faucet type.
Key Point 3: Understanding the Function of the Diverter
The diverter is a key component in bathtub faucets equipped with a showerhead. Its primary function is to redirect the water flow from the tub spout to the showerhead, allowing the user to switch between taking a bath and a shower.
The diverter mechanism varies depending on the faucet design. In some faucets, the diverter is a simple lever or knob located on the spout. When the lever is pulled up or the knob is turned, it closes off the opening to the spout and redirects the water flow to the showerhead. Other faucets utilize a push-button diverter, which operates on a similar principle.
Internally, the diverter typically consists of a valve or gate that moves to block or allow water flow to the spout. This valve is often made of rubber or plastic and is designed to create a watertight seal. Over time, the diverter valve can wear out or become clogged with mineral deposits, leading to a leak from the spout even when the shower is in use.
Diagrams detailing the diverter mechanism would show its internal components and how they interact to redirect the water flow. The diagram would highlight the location of the diverter valve, the seals that prevent leaks, and the linkage that connects the lever or knob to the valve. Understanding the diverter mechanism is crucial for troubleshooting issues such as a leaky spout or a diverter that does not stay engaged.
Beyond the specific components already discussed, it's worth mentioning other hardware elements that contribute to the overall functionality and installation of the bathtub faucet. Supply lines, typically flexible metal or plastic hoses, connect the faucet to the hot and cold water supply pipes. These lines often include shut-off valves that allow the water supply to be turned off for maintenance or repairs. Mounting brackets and hardware secure the faucet to the bathtub or surrounding surface, ensuring stability and preventing movement. Plumber's tape or pipe dope is used to seal threaded connections and prevent leaks. Understanding the role of these additional components contributes to a comprehensive understanding of the bathtub faucet system.
In conclusion, a bathtub faucet, despite its outward simplicity, is a complex assembly of meticulously engineered parts. Recognizing the function and interrelation of these parts empowers homeowners to troubleshoot problems and perform basic repairs. While specific designs may differ according to faucet type, a fundamental understanding of the handles, spout, valve body, diverter, and associated hardware is indispensable for anyone seeking to maintain or upgrade their bathroom fixtures.

Bathtub Parts Everyone Should Know About Part Names 2024

Learn How To Remove And Install Various Tub Spouts

Parts Of Shower Valve Name Diagram Linquip

Learn How To Remove And Install Various Tub Spouts

Bath Tub Spouts The Largest Selection Of On Web

15 Essential Parts Of A Bathtub And How They Work

The Diffe Parts Of A Bathtub And How They Work Family Handyman

Polished Chrome Courant 8p8 Ws2 Cospc 1 Handle Tub Shower Trim With Valve Pfister Faucets

Ultimate Guide On 24 Parts Of A Bathtub Names Functions Diagram

Parts Of A Bathtub With Diagram Homenish